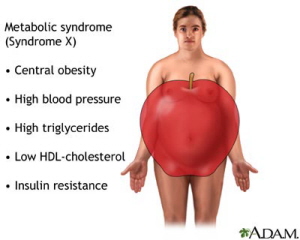
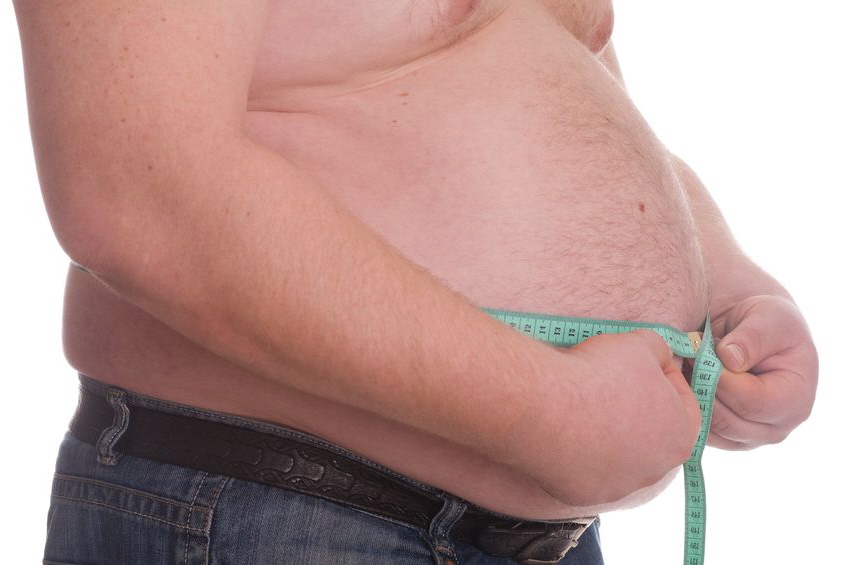
Pre-Diabetes Risk Factors
The American Diabetes Association recommends that testing to detect pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes be considered in adults without symptoms who are overweight or obese and have one or more additional risk factors for diabetes. In those without these risk factors, testing should begin at age 45. Risk factors for pre-diabetes and diabetes—in addition to being overweight or obese or being age 45 or older—include the following…