
 Blood glucose monitoring refers to testing how much glucose is in the blood stream (or, glycemia.) Many people often refer to blood glucose as “blood sugar” because glucose is a form of sugar. Although the proper medical term is “glucose” your doctor will know what you mean if you use the term blood sugar.
Blood glucose monitoring refers to testing how much glucose is in the blood stream (or, glycemia.) Many people often refer to blood glucose as “blood sugar” because glucose is a form of sugar. Although the proper medical term is “glucose” your doctor will know what you mean if you use the term blood sugar.
Why do people need to test their blood glucose levels?
When you eat food or drink beverages containing calories your body converts what you ingest into glucose, a form of sugar the body needs to nourish cells, tissues, and organs.  Insulin is required by the body to move glucose from the blood stream into cells and tissues. Insulin is made by the pancreas and acts like a key, opening cells to receive glucose. If your body does not make enough insulin to move glucose from the blood stream into cells, glucose levels can build up to unsafe levels in the bloodstream.
People who may have metabolic problems with insulin production or insulin resistance, include women with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, pre-diabetes, and other forms of diabetes including cystic fibrosis related diabetes, hemochromatosis (bronze diabetes), maturity onset diabetes of the young, and latent autoimmune diabetes in adults.
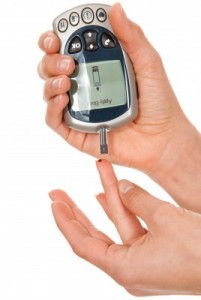
How do I test my blood glucose (sugar)?
Home blood glucose meters can be used measure your blood glucose levels.  Depending on the type and brand of meter you use, you take a small sample of blood using a lancing device from a finger, toe, forearm, or ear lobe. Where you take your blood sample will affect test results and most experts recommend you always use your finger tips for the most accurate results.
A test strip is placed inside the blood glucose meter (you can ONLY use test strips designed for your particular meter but you can use any lancing device to draw blood for the sample.) A drop of blood is then placed on the strip.  Blood reacts with chemicals in the test strip causing a small electronic pulse to be sent into the meter which then calculates the level of glucose in the blood sample and shows the result in a digital display.
How often should I test my blood glucose?
Your doctor will tell you how often you should test your blood sugar. People who take insulin, typically test five to ten or more times each day. People who take medications to lower their blood glucose levels, like those with type 2 diabetes, typically test three to five times each day.
If you have been diagnosed with pre-diabetes and are not on any medications your doctor may have you test once a day in the morning before eating, or even as little as once a week. Whatever your doctor advises be sure to at least test as often as she/he suggests. While it will not hurt you to test more frequently, it may not be necessary and test
Medical Terms
- Hypoglycemia is the medical term for low blood glucose;
- Hyperglycemia refers to high blood glucose; and
- Normoglcyemia indicates normal blood glucose levels.
Units of Measurement
In the United States, blood glucose is measured in mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). Â In Europe and most other countries, blood glucose is measured in mmol/L.


